Unlock the Hidden Power of Functional Medicine to Beat Autoimmune Diseases
Autoimmune diseases affect an estimated 50 million Americans, causing a myriad of health issues and impacting the quality of life for those afflicted. These conditions occur when the immune system, which is designed to protect the body from external threats, mistakenly attacks its own healthy tissues. Autoimmune diseases encompass over 100 recognized conditions. Some well-known examples include rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, multiple sclerosis, and type 1 diabetes. While each autoimmune disease may manifest differently, they all share common underlying factors.
In this in-depth exploration, we will delve into the world of autoimmune diseases, examining their diagnosis, symptoms, and conventional medical approaches. More importantly, we will explore the functional medicine perspective, which seeks to address the root causes of these conditions, offering hope for prevention, reversal, and effective management. By the end of this comprehensive guide, you will have a profound understanding of autoimmune diseases and the tools to take control of your health or support a loved one on their journey to well-being.
Understanding Autoimmune Diseases: What Are They?
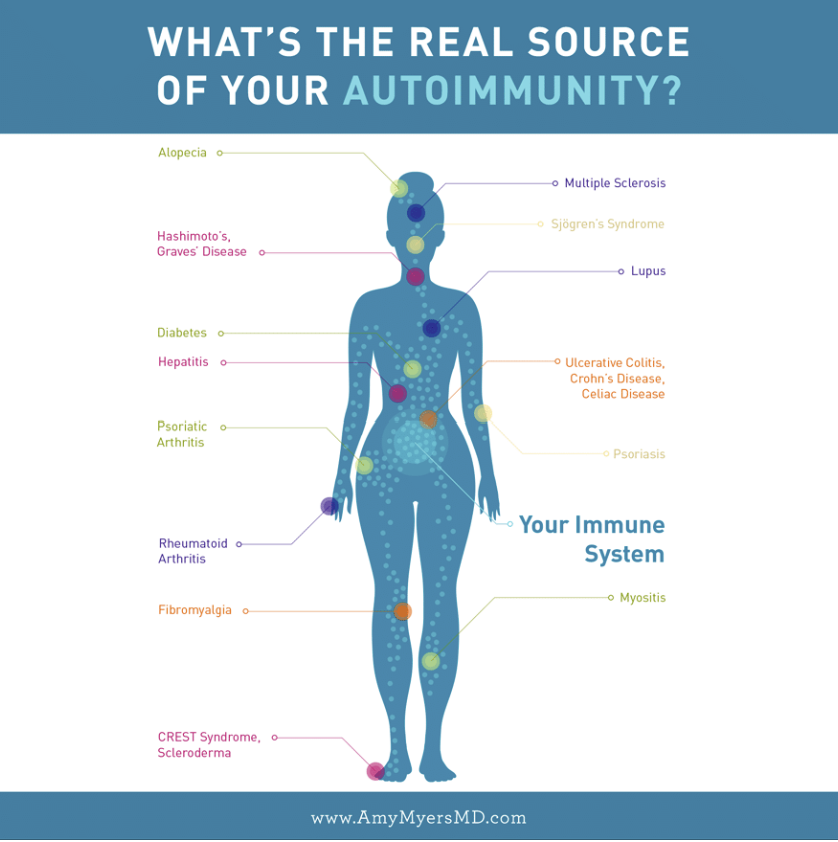
Autoimmune diseases are a group of disorders characterized by the immune system mistakenly attacking the body’s healthy tissues. These conditions can affect various organs and systems, leading to a wide range of symptoms. Over 100 autoimmune diseases have been identified. Some of the most well-known ones include rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, multiple sclerosis, and type 1 diabetes.
Autoimmune diseases are categorized based on the specific tissues or organs that the immune system targets. For instance, in Sjogren’s syndrome, the immune system attacks cells responsible for tear and saliva production. Resulting symptoms are dry eyes and a dry mouth. Alopecia areata leads to the immune system attacking hair follicles, causing hair loss and bald patches. Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and Grave’s disease both involve the immune system targeting the thyroid gland, leading to issues with thyroid hormone production and various associated symptoms.
Diagnosing Autoimmune Diseases
Diagnosing autoimmune diseases can be a challenging and time-consuming process. These conditions often develop slowly over years or even decades. This often makes it difficult to pinpoint the exact cause of mysterious symptoms. It is estimated that individuals with severe autoimmunity may go four years or more without a proper diagnosis!
One complicating factor in diagnosing autoimmune diseases is the overlap and variability in symptoms among different conditions. Additionally, around 25 percent of people with one autoimmune disease will eventually develop another, a phenomenon known as multiple autoimmune syndrome (MAS). For example, individuals with Sjogren’s syndrome often also have lupus or rheumatoid arthritis.
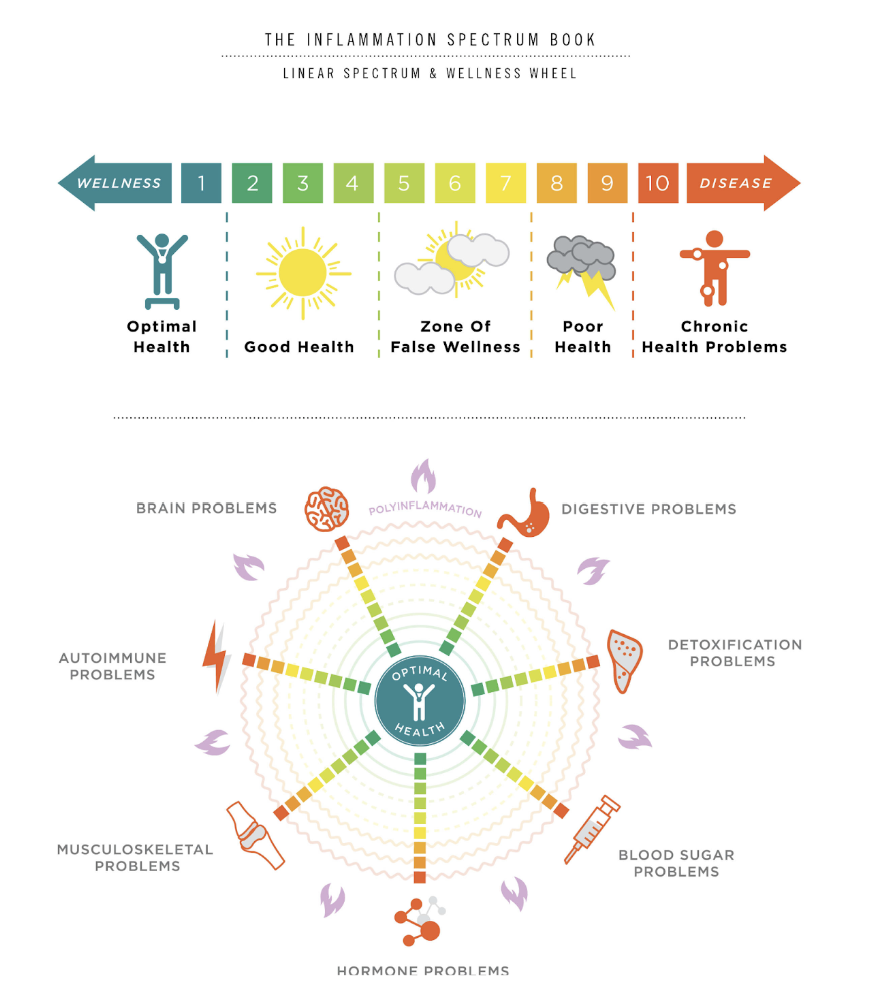
Autoimmune diseases are inherently inflammatory. And, there are numerous warning signs to be aware of, including acne, allergies, joint pain, fatigue, brain fog, mood imbalances, digestive issues, headaches, migraines, sleep problems, and skin conditions. While conventional medicine often views autoimmune diseases as a binary presence or absence, functional medicine considers them as a SPECTRUM.
Functional medicine recognizes three stages of autoimmune disease:
- Low inflammation and higher stress tolerance
- High inflammation with major symptoms
- Immune system goes into overdrive, leading to a full-blown autoimmune disease
Patients typically seek medical help when they are somewhere between the middle and far end of this spectrum. However, early detection of inflammatory signs and proactive lifestyle interventions can significantly slow or prevent the progression of autoimmune diseases.
When autoimmune disease is suspected, a common initial step is testing for antinuclear antibody (ANA) to confirm that the immune system is indeed attacking its own cells. Subsequently, a comprehensive autoimmune panel is conducted to identify the type and origin of the autoimmunity. If diagnosed with ANA or a specific autoimmune condition, interventions can help prevent further deterioration and even reverse the condition. For those yet undiagnosed, adopting a healthy lifestyle is crucial to maintain a balanced immune system and overall well-being.
Functional Medicine vs. Conventional Approaches to Treating Autoimmune Disorders
Conventional medicine typically focuses on detecting autoimmune diseases, identifying their specific type, and managing symptoms with pharmaceuticals, including immunosuppressants and pain medications. In contrast, functional medicine aims to address the ROOT CAUSES of autoimmune diseases.
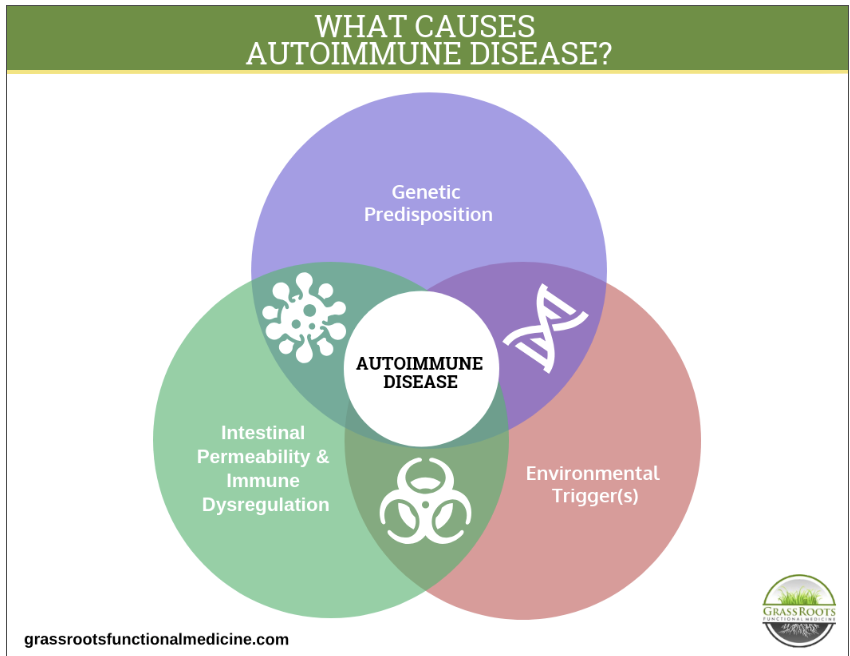
The root causes of autoimmune disease can be divided into three primary categories: genetic predisposition, impaired digestive health, and environmental triggers. While we cannot change our genetic predisposition, research indicates that it accounts for only 30 percent of autoimmune conditions. The remaining 70 percent of contributors are environmental, making them modifiable through lifestyle choices.
The Gut-Autoimmune Connection
One significant contributor to autoimmune diseases is gut health, which we have the power to repair and optimize. Research shows that approximately 80 percent of our immune system resides in the gut, highlighting the importance of gut health in immune function.
One key aspect of gut dysfunction is intestinal permeability, often referred to as “leaky gut.” The intestinal lining, just one cell thick, serves as a barrier between the contents of the gut and the bloodstream. When the tight junctions between these cells become compromised and allow unwanted particles to leak into the bloodstream, the immune system becomes overwhelmed. It starts to identify not only harmful compounds but also normally harmless substances, leading to inaccurate immune responses and ultimately targeting healthy tissue.
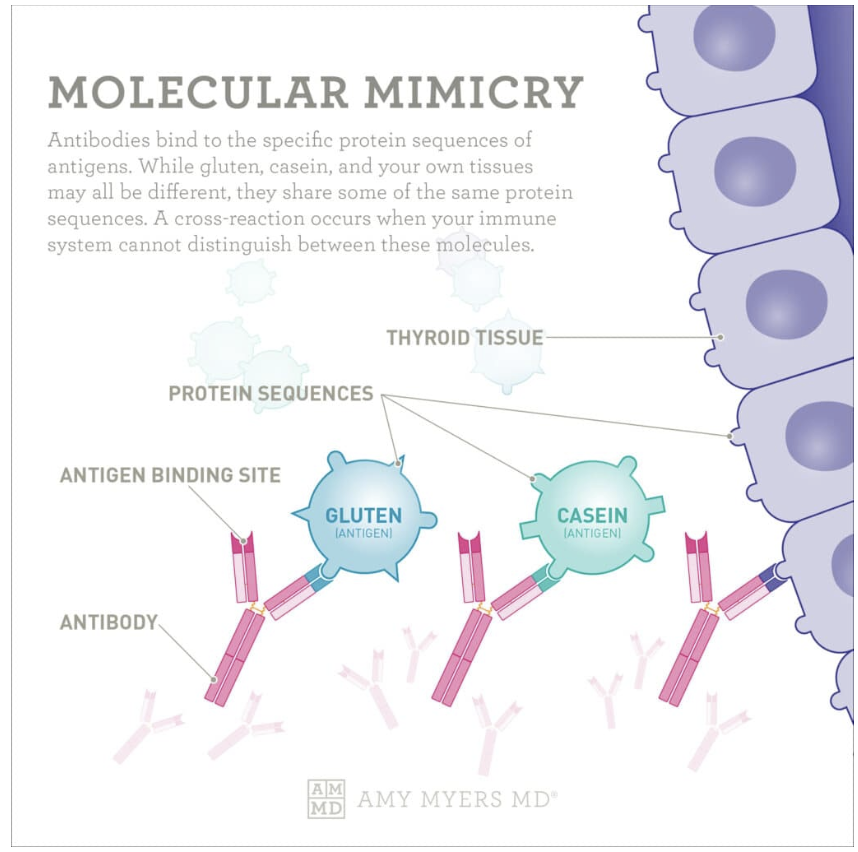
Molecular mimicry exacerbates this problem, as the immune system mistakes proteins in food for its own cells and attacks them. Gluten and dairy are common triggers for molecular mimicry.
Intestinal dysbiosis, an imbalance of gut microbes, also significantly contributes to autoimmune diseases. A healthy microbial ecosystem in the gut plays a crucial role in nutrient breakdown, synthesis of essential compounds, and overall health protection. Disruptions in this ecosystem can lead to leaky gut, a known autoimmune trigger.
To protect the gut from dysbiosis and intestinal permeability, the “5R” approach is applied:
- REMOVE harmful foods, behaviors, and lifestyle factors, such as gluten, dairy, alcohol, and gut irritants.
- REPLACE essential compounds that may be depleted due to excess inflammation and immune system overactivity.
- REPLENISH the gut with prebiotic- and probiotic-rich foods once tolerance is regained.
- REPAIR the gut lining with anti-inflammatory foods and targeted supplements.
- REBALANCE lifestyle factors to minimize symptoms, maintain remission, and optimize overall health.
Environmental Triggers in Autoimmune Disease
Environmental and lifestyle factors, unique to each individual, also contribute to autoimmune diseases. While we all face different stressors and have varying tolerance levels, we can modify our lifestyles to minimize their impact and reduce the risk of autoimmune diseases.
Dietary stressors are one of the leading triggers for autoimmune diseases, as unhealthy eating choices can exacerbate inflammation – the root of these conditions. The autoimmune protocol (AIP) diet, for example, has shown promise as a nutritional therapy for autoimmune diseases. It involves eliminating inflammatory foods for a minimum of four weeks and gradually reintroducing them to test for tolerance.
Another significant environmental factor is toxins. In our modern world, we are exposed to a plethora of toxins through the air, water, food, and skin. These toxins include heavy metals, herbicides, pesticides, endocrine disruptors, and chemicals found in skincare products.
Reducing exposure to environmental toxins is crucial, and resources like the Environmental Working Group (EWG) offer guidance on clean product alternatives. Additionally, supporting the body’s natural detoxification systems is essential. Our liver, kidneys, and digestive tract play critical roles in eliminating toxins, and a healthy diet rich in specific nutrients supports these processes.
Managing Mental-Emotional Stress
Psychological stress is another lifestyle factor strongly linked to autoimmune diseases. Although the exact mechanisms remain unclear, stress has been established as a significant contributor to the onset and exacerbation of these conditions. Research indicates that up to 80 percent of individuals with autoimmune diseases reported high stress levels when their symptoms first appeared.
Stress can increase the production of cytokines, immune-modulating proteins involved in the body’s inflammatory response. While the perception and tolerance of stress vary among individuals, the biological response to stress is consistent, leading to increased inflammation.
Managing stress is vital to autoimmune disease prevention and management. Strategies such as therapy, meditation, journaling, and spending time with loved ones can help individuals cope with stress proactively. Developing effective stress management practices is crucial to prevent stress from negatively impacting health.
Our Role in Autoimmune Disease
Understanding the key pillars of autoimmune diseases – genetic predisposition, gut health, and environmental lifestyle factors – empowers individuals to take control of their health. While complete control over every aspect of these conditions may not be possible, adopting healthy eating habits, managing stress, and minimizing toxic exposure hold significant potential for improving health and well-being.
Embarking on the journey to reverse symptoms and live a healthier, more fulfilling life can be overwhelming. Seeking professional guidance, such as health coaching, can help individuals navigate the complexities of autoimmune diseases. Personalized plans tailored to individual needs can fast-track progress and provide invaluable support on the path to well-being.
Health coaching or working with a functional medicine practitioner can help you find your personalized path to health and empower you to lead a life of vitality and fulfillment. Your health matters, and we are here to guide you every step of the way.
If you’re ready to take control of your health or support a loved one on their journey to wellness, consider booking a FREE 30-minute call with Rachel Scheer Nutrition.

Rachel Scheer is a Certified Nutritionist who received her degree from Baylor University in Nutrition Science and Dietetics. Rachel has her own private nutrition and counseling practice located in McKinney, Texas. Rachel has helped clients with a wide range of nutritional needs enhance their athletic performance, improve their physical and mental health, and make positive lifelong eating and exercise behavior changes.
Read This Next
Micronutrients, or the vitamins and minerals your body needs, typically work like a team. To…
If you want to improve gut health, or even optimize your overall health, you’ve probably…
Have you ever found yourself grappling with the discomfort of abdominal distension, bloating, or cramping,…